HTML5 之音频合成(Speech Synthesis)
H5 让我们的 Web 交互更加生动有趣,但浏览器的多样性以及挥之不去的兼容问题,却阻碍了技术发展。这并不是我们拒绝的理由,恰恰相反,它应该成为动力。
一、语音场景
文章标题为了严谨,所以叫音频合成。如果用大白话来解释,那就是「文字转语音」。语音的场景就太多了:
- 点读机:哪里不会点哪里
- 有声小说:看着太累,听起来不错
Web页面警示用户的操作- 闹钟,提醒,小秘书
- 残疾人支持
…
这些都是随处可见的例子,但真正燃起我激情的是这个场景,简直酷炫到爆。原来动画和语音结合起来才是最佳的用户体验。
二、技术核心
看完上面的动画,按捺不住内心的好奇,随手就翻起了源码。Oh~原来如此,把你揪出来:1
2let sayhello = new window.SpeechSynthesisUtterance('你好,欢迎来到 Jartto 的博客!');
window.speechSynthesis.speak(sayhello);
事情的真相就是简单如此,短短两行,就实现了语音播报。
三、兼容性
如此有趣的 API,突然想到了一万个应用场景。别忙,先来看看 SpeechSynthesis 的兼容性吧: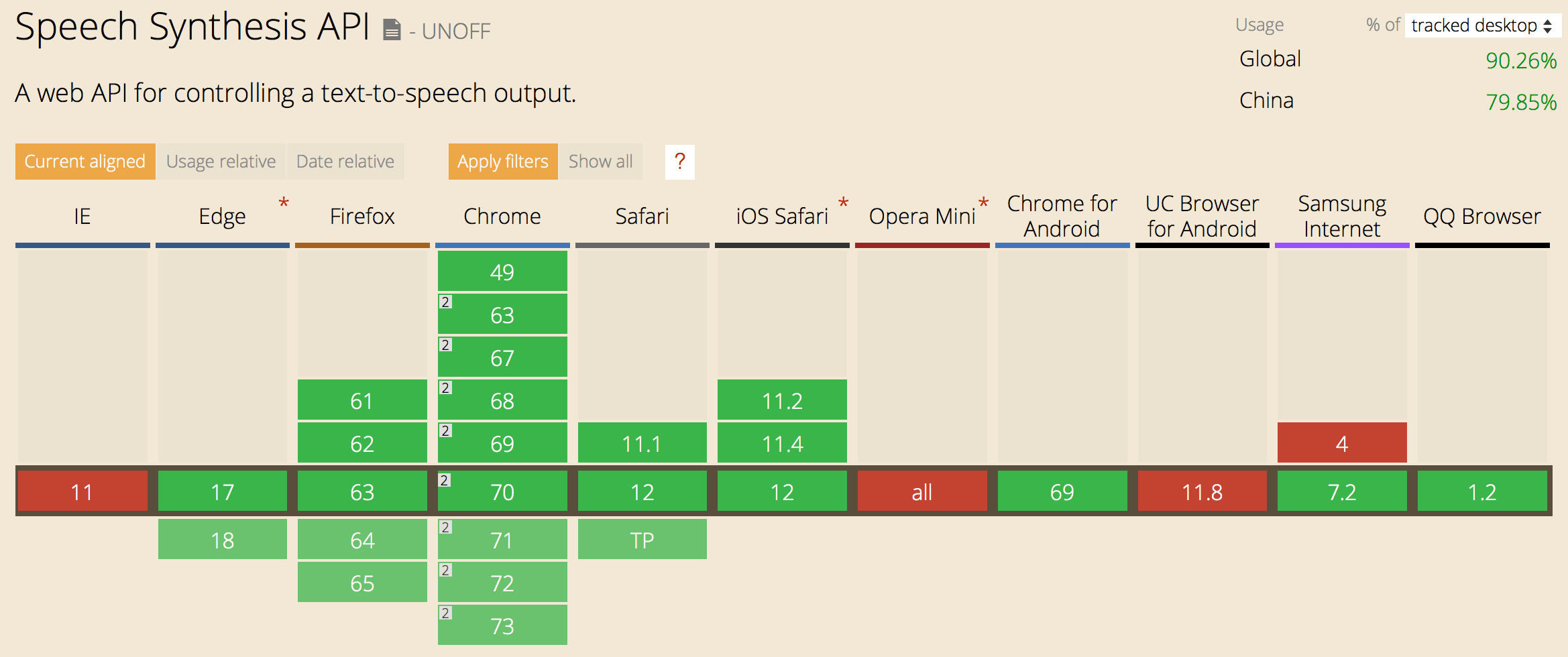
看起来各大浏览器支持的还不错,那就试试呗!
四、API 文档
SpeechSynthesis 接口是语音服务的控制接口,属于网页语音 API,它可以用于获取设备上关于可用的合成声音的信息,开始、暂停语音,或除此之外的其他命令。
既然浏览器已经普遍支持了,那么我们不妨打印出来看看。

下面我们来适当的解释一下:
- SpeechSynthesis.paused: 当
SpeechSynthesis处于暂停状态时,Boolean值返回true。 - SpeechSynthesis.pending: 当语音播放队列到目前为止保持没有说完的语音时,
Boolean值返回true。 - SpeechSynthesis.speaking: 当语音谈话正在进行的时候,即使
SpeechSynthesis处于暂停状态,Boolean返回true。 - SpeechSynthesis.onvoiceschanged: 当由
SpeechSynthesis.getVoices()方法返回的SpeechSynthesisVoice列表改变时触发。
此外,还有几个非常实用的方法:
- SpeechSynthesis.cancel(): 移除所有语音谈话队列中的谈话。
- SpeechSynthesis.getVoices(): 返回当前设备所有可用声音的
SpeechSynthesisVoice列表。 - SpeechSynthesis.pause(): 把 SpeechSynthesis 对象置为暂停状态。
- SpeechSynthesis.resume(): 把 SpeechSynthesis 对象置为一个非暂停状态:如果已经暂停了则继续。
- SpeechSynthesis.speak(): 添加一个 utterance 到语音谈话队列;它将会在其他语音谈话播放完之后播放。
API 很简单,这里就不赘述了,来个例子尝尝鲜。
五、代码演示
MDN Web Docs上面有个很形象的例子,我们拿过来学习学习:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20var synth = window.speechSynthesis;
var voices = synth.getVoices();
if (synth.speaking) {
console.error('Speaking');
return;
}
var sayThis = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance('你好,欢迎来到 Jartto 的博客!');
sayThis.onend = function (event) {
console.log('End');
}
sayThis.onerror = function (event) {
console.error('Error');
}
sayThis.pitch = pitch.value;
sayThis.rate = rate.value;
synth.speak(sayThis);
注意:这里为了演示,只列出了核心代码,完整代码请看下面「完整示例」。
六、完整示例
看完了核心代码,这里把完整代码贴出来,整理理解一下,加强记忆吧:
1.html1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21<form>
<input type="text" class="txt">
<div>
<label for="rate">Rate</label>
<input type="range" min="0.5" max="2" value="1" step="0.1" id="rate">
<div class="rate-value">1</div>
<div class="clearfix"></div>
</div>
<div>
<label for="pitch">Pitch</label>
<input type="range" min="0" max="2" value="1" step="0.1" id="pitch">
<div class="pitch-value">1</div>
<div class="clearfix"></div>
</div>
<select>
</select>
<div class="controls">
<button id="play" type="submit">Play</button>
</div>
</form>
2.js1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81var synth = window.speechSynthesis;
var inputForm = document.querySelector('form');
var inputTxt = document.querySelector('.txt');
var voiceSelect = document.querySelector('select');
var pitch = document.querySelector('#pitch');
var pitchValue = document.querySelector('.pitch-value');
var rate = document.querySelector('#rate');
var rateValue = document.querySelector('.rate-value');
var voices = [];
function populateVoiceList() {
voices = synth.getVoices();
var selectedIndex = voiceSelect.selectedIndex < 0 ? 0 : voiceSelect.selectedIndex;
voiceSelect.innerHTML = '';
for(i = 0; i < voices.length ; i++) {
var option = document.createElement('option');
option.textContent = voices[i].name + ' (' + voices[i].lang + ')';
if(voices[i].default) {
option.textContent += ' -- DEFAULT';
}
option.setAttribute('data-lang', voices[i].lang);
option.setAttribute('data-name', voices[i].name);
voiceSelect.appendChild(option);
}
voiceSelect.selectedIndex = selectedIndex;
}
populateVoiceList();
if (speechSynthesis.onvoiceschanged !== undefined) {
speechSynthesis.onvoiceschanged = populateVoiceList;
}
function speak(){
if (synth.speaking) {
console.error('speechSynthesis.speaking');
return;
}
if (inputTxt.value !== '') {
var utterThis = new SpeechSynthesisUtterance(inputTxt.value);
utterThis.onend = function (event) {
console.log('SpeechSynthesisUtterance.onend');
}
utterThis.onerror = function (event) {
console.error('SpeechSynthesisUtterance.onerror');
}
var selectedOption = voiceSelect.selectedOptions[0].getAttribute('data-name');
for(i = 0; i < voices.length ; i++) {
if(voices[i].name === selectedOption) {
utterThis.voice = voices[i];
}
}
utterThis.pitch = pitch.value;
utterThis.rate = rate.value;
synth.speak(utterThis);
}
}
inputForm.onsubmit = function(event) {
event.preventDefault();
speak();
inputTxt.blur();
}
pitch.onchange = function() {
pitchValue.textContent = pitch.value;
}
rate.onchange = function() {
rateValue.textContent = rate.value;
}
voiceSelect.onchange = function(){
speak();
}
3.css1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54.txt, select, form > div {
display: block;
margin: 0 auto;
font-family: sans-serif;
font-size: 16px;
padding: 5px;
}
.txt {
width: 80%;
}
select {
width: 83%;
}
form > div {
width: 81%;
}
.txt, form > div {
margin-bottom: 10px;
overflow: auto;
}
.clearfix {
clear: both;
}
label {
float: left;
width: 10%;
line-height: 1.5;
}
.rate-value, .pitch-value {
float: right;
width: 5%;
line-height: 1.5;
}
#rate, #pitch {
float: right;
width: 81%;
}
.controls {
text-align: center;
margin-top: 10px;
}
.controls button {
padding: 10px;
}
七、补充:SpeechRecognition
既然提到了文字转语音,那么不得不提到语音识别。
SpeechRecognition 顾名思义,语音识别,属于网页语音 API。需要麦克风等音频输入设备的支持,可以识别用户的语音输入,并且转化成文字。
SpeechRecognition API 需要硬件支持,所以兼容性并不好,大致如下: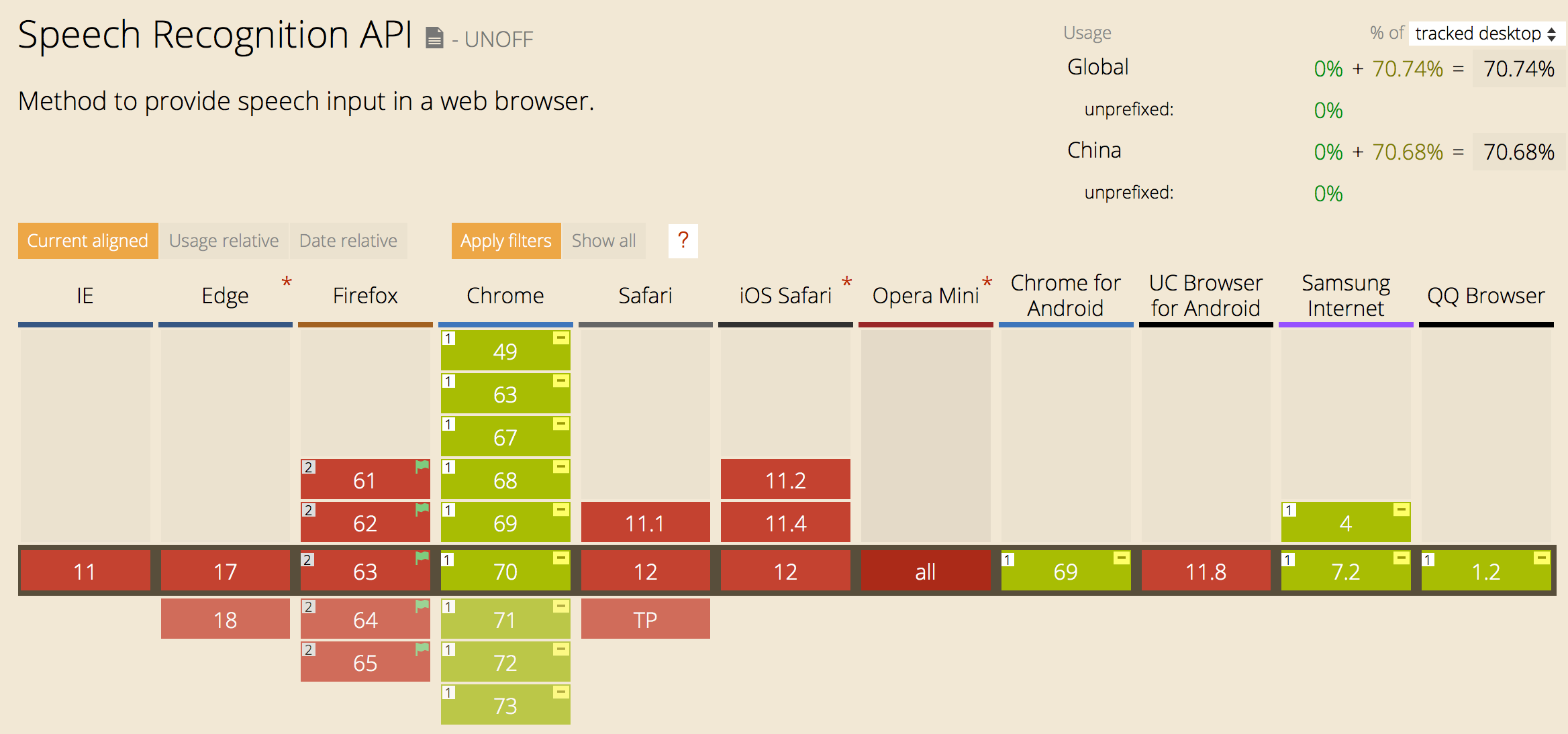
八、未来畅想
相信不久的未来,浏览器会逐步统一,兼容问题将会化为乌有。我们将会用更多的时间去探索技术,而不是去兼容老破旧的网站或者机器。当然,Web 技术会大行其道,用户将会拥有到更加有趣的体验。今天,我们迈进了一步!

